Are you still foolishly using ordinary PE plastic bags to pack hot food?
In contemporary society, many people are still accustomed to using ordinary plastic bags to pack hot food. This behavior may seem convenient, but it may pose a double threat to health and the environment. By exploring the impact of heat resistance of plastic bags, we can better understand the risks and countermeasures behind them.
Plastic bag material and heat resistance
Common materials for plastic bags on the market include polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP).
The most common PE plastic bags are LDPE low-density polyethylene. The heat-resistant temperature of LDPE is usually below 80°C, while that of PP plastic bags is slightly higher and can withstand around 100°C. However, when the temperature exceeds the upper limit of the material's heat resistance, plastic bags may release toxic substances, such as chemicals such as bisphenol A or phthalates, which are potentially harmful to human health.
If you put boiling soup or hot food out of the oven into plastic bags, these chemicals may seep into the food and be further absorbed by the human body. Long-term exposure to these harmful substances may lead to endocrine disorders, increased cancer risk and other chronic diseases. This shows that choosing the right container for hot food is crucial to ensuring health.
In the polyethylene (PE) segment, LDPE (low-density polyethylene) and HDPE (high-density polyethylene) are the two main subtypes, with slightly different heat resistance properties and application ranges.
Differences between LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) and HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
According to the figure below, we can know the continuous heat-resistant temperature of different plastic materials, that is, the temperature at which they can be used.
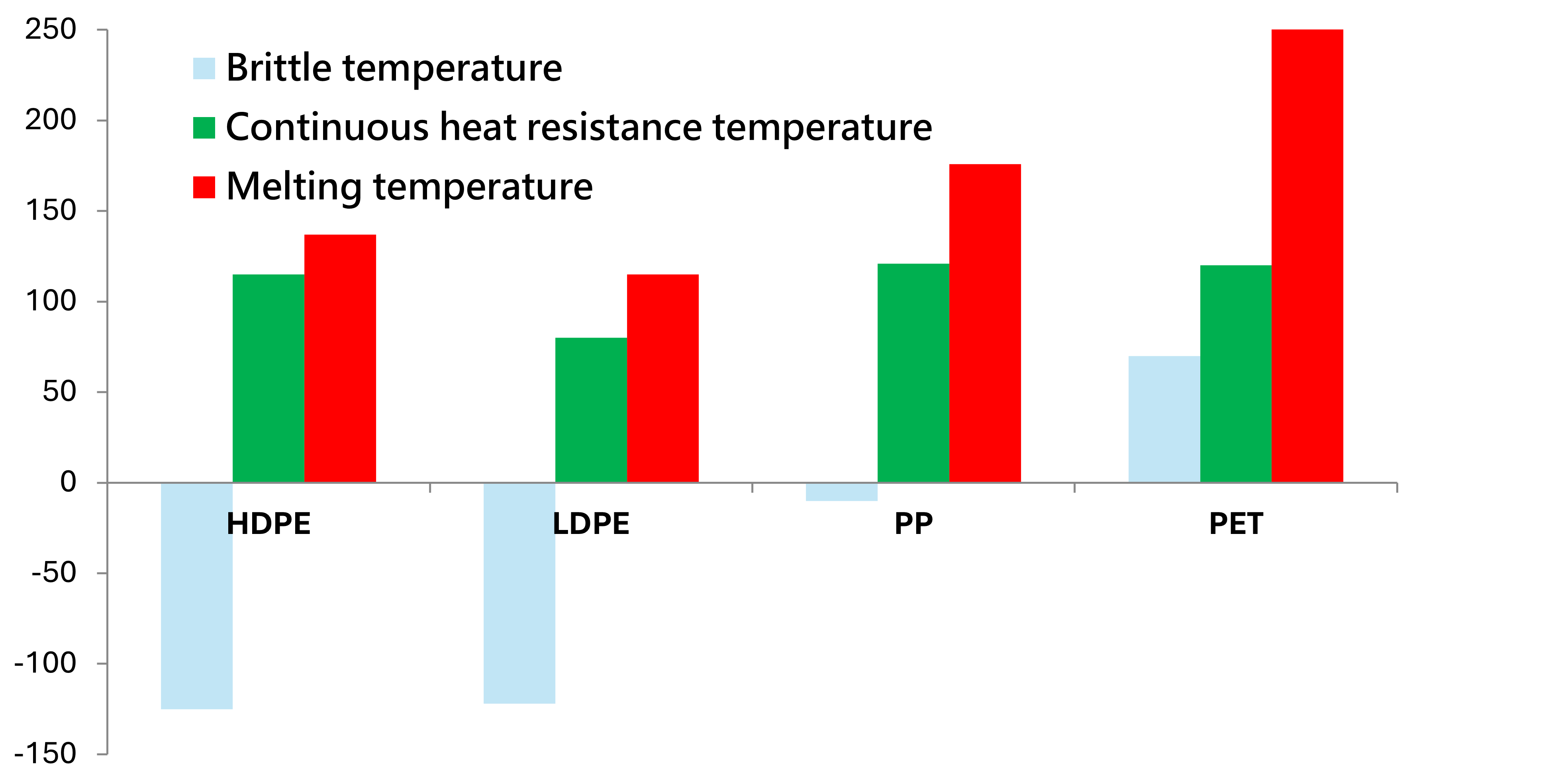
LDPE (Low Density Polyethylene)
Characteristics and heat resistance:
LDPE has the characteristics of high softness and good transparency, so it is often used to make food packaging bags and plastic films. Its heat-resistant temperature is approximately between 60℃ and 80℃, which makes it suitable for cold food or food at room temperature, but it is not suitable for directly holding hot soup or hot food, as high temperatures may cause the material to deform or release harmful chemicals.
Application areas:
LDPE is very common in daily life, such as supermarket shopping bags, refrigerated bags, plastic wrap, etc. Due to its low density, it is easier to shape and process, but at the same time, due to its low heat resistance, special care should be taken when using it.
HDPE (High-density polyethylene)
Characteristics and heat resistance:
HDPE has a tighter structure and higher density, making it more rigid and durable than LDPE. Its heat-resistant temperature is usually between 95℃ and 115℃, making it more suitable than LDPE for packaging foods with slightly higher temperatures. However, even so, HDPE is still not recommended to be used to directly hold boiling hot soup or greasy food to avoid health risks.
Application areas:
HDPE is often used to make milk bottles, plastic buckets, water pipes and food-grade plastic containers. Its chemical and heat resistance make it a reliable choice for food packaging, but attention should still be paid to its applicability in high temperature environments.
Distinguishing LDPE (low-density polyethylene) from HDPE (high-density polyethylene) can be done from the following aspects:
1. Appearance and texture
- LDPE: It has a soft texture and high transparency, usually showing a slightly milky translucent effect. It feels elastic and can be easily folded or stretched.
- HDPE: Relatively hard, opaque or milky white, feels firm and does not wrinkle easily when folded.
2. Density and weight
- LDPE: Lower density, lighter weight, feels thinner.
- HDPE: It has a higher density, is relatively heavy, and is thick. It is often used in heavy-duty plastic bags or food-grade containers.
3. Compression resistance and durability
- LDPE: It is very soft but has poor compression resistance and can be easily punctured or torn.
- HDPE: high rigidity, superior compression resistance, more wear and tear resistance.
4. Heat resistance
- LDPE: The heat resistance temperature is about 60℃ to 80℃, which is suitable for cold food or room temperature food, but not suitable for high temperature use.
- HDPE: The heat-resistant temperature is about 95℃ to 115℃. It is more suitable for contact with slightly hot food than LDPE, but it still needs to be avoided to directly hold boiling hot soup.
5. Combustion method
If direct identification is not possible, a combustion test is an effective method:
- LDPE: It has a light blue flame, a waxy smell, and melts quickly.
- HDPE: Burns with a yellow-blue flame, smells like wax but thicker, and melts more slowly.
6. Voice Recognition
- LDPE: There is almost no sound when you pinch or pull the plastic bag.
- HDPE: When you rub a plastic bag, it will produce a noticeable rustling sound.
Through the above methods, we can more intuitively distinguish the material properties of LDPE and HDPE, making it easier to choose more suitable materials to hold hot food in daily life.