Overmolding
Introduction to overmolding
Overmolding is a special injection molding process. Most overmolding is a thermoplastic elastomer plastic, collectively called TPE. Common names on the market include TPE, TPR, and TPU. etc., molded onto the outside of another part (base material or body). This type of base material body parts has its own special structural requirements or strength requirements, such as hooks, buckles, different shape requirements, screw posts for locking, connection strength with other parts, folding resistance, and durability, pressure, deformation resistance, etc. This part is usually a plastic part made using the injection molding process. Depending on the needs of different products, it can also be made of various other non-plastic materials, such as metal parts, ceramic parts, wood Parts and more. Due to its excellent characteristics, overmolding is widely used in various industries and has many different uses.
The following are common application requirements for overmolding:
Advantages of Overmolding
- Improved touch: In the actual use of various products on the human body, compared to the hard materials of plastic, which are bound by hard materials, there is a little less soft touch, or the cold metal materials, which are less warm to the touch, so the tactile comparison of the products is Next, if overmolding can be used, the texture and visual appearance of the product can be greatly improved.
- Anti-slip effect: Generally speaking, when using various tools, especially hand tool products, these products are parts with handles. Usually, something is needed to help the operator maintain the corresponding grip and appropriate position during use. The tightening effect is maintained on the operator's hand. The over-molded grip handle can greatly enhance the grip, especially in wet and slippery conditions, making it safer for the operator, relatively effortless to use, and providing better tool controllability.
- Shock absorption function: Plastic elastomer is similar to rubber and has certain shock absorption and buffering effects. On highly sensitive components, its type of intermediate material or mounting base can protect its electronic components (such as high-end electronic equipment) from Damaged by vibration.
- Comfortable operation: The shells of grip products or related electronic parts are injection molded and can be molded into any shape according to the way your fingers are held. They can also be integrated into aesthetic designs to achieve a high-quality product that is very ergonomic.
- Sealing: In the face of dust-proof and waterproof requirements, it is difficult for hard materials to achieve a high degree of dust-proof and waterproof effects. Therefore, the product design, coupled with injection overmolding, can be widely used in electronic equipment and other outdoor equipment, achieving waterproof and dustproof sealing.
- Sound absorption effect: Polymer plastic elastomers have relatively loose connections between their molecules, and their soft properties can reduce the resonance, resonance and transmission of sound waves, and have the same shock-absorbing and sound-absorbing effect as foam products, so sound waves can be absorbed through the overmolded material.
Overmolding materials
TPE: Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
It has the functions and properties of traditional thermosetting rubber: soft, elastic, good touch and other advantages that ordinary plastics do not have. It also has the dual advantages of thermoplastic plastics being easy to process, fast and recyclable. TPE is a thermoplastic that has been specially designed and modified to rubberize its functions and properties. Therefore, it is also called Thermoplastic Rubbers, or TPR for short.
The future development trend of TPE is to replace many uses of rubber other than tires, and to replace some soft PVC, such as automotive materials, oil seals, piping, wire and cable insulation coatings, medical equipment, etc.
The softness and hardness of thermoplastic elastomers can be adjusted according to the use requirements. In different fields or operating environment conditions, the difference in softness and hardness will greatly affect its operability, safety and comfort. The softness and hardness of thermoplastic elastomers Adjustability is a major advantage, and its application fields are relatively wide.
The figure below shows the hardness distribution range of thermoset rubber, thermoplastic elastomer and thermoplastic plastic. The black on the left is thermoset rubber, the blue in the middle is thermoplastic elastomer, and the orange on the right is thermoplastic.
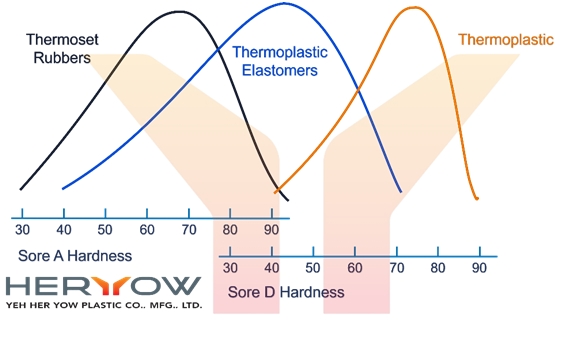
Thermoplastic elastomer can be melted by heating and solidified by cooling. It is different from ordinary rubber in its one-time processability. Thermoplastic elastomer can be processed repeatedly. But its characteristic is that it is soluble in some specific solvents and has meltable and soluble properties. Thermoplastic plastics are easy to mold and process, but have low heat resistance and are prone to creep (creep) during back-end use. The degree changes with the load, ambient temperature, solvent, and humidity. Therefore, it is often used in overmolding designs, using thermoplastic plastic as its body or base material to avoid deformation under long-term use.
Material properties:
- Stretch properties
Most material data sheets will have various properties related to tensile strength, elongation, tensile modulus, etc. Tensile properties show how a material performs under tensile conditions. - Compression characteristics
Since TPE plastic is most commonly used due to its flexibility, knowing how much a part can compress without causing permanent damage is important for product considerations. - Friction coefficient
Friction is the amount of force required to move one surface to another. Different types of TPE have different friction coefficients. - Hardness
The hardness property is the ability of a material to resist indentation because the hardness of different materials varies greatly. The "hardness" of the material is usually related to the touch feel of TPE plastic, but if the flexural modulus can be considered together, a better touch choice will be achieved. - Flexural modulus
The material's ability to resist bending is its flexural modulus. This characteristic is the second major factor in TPE's "feel". - Classification of materials
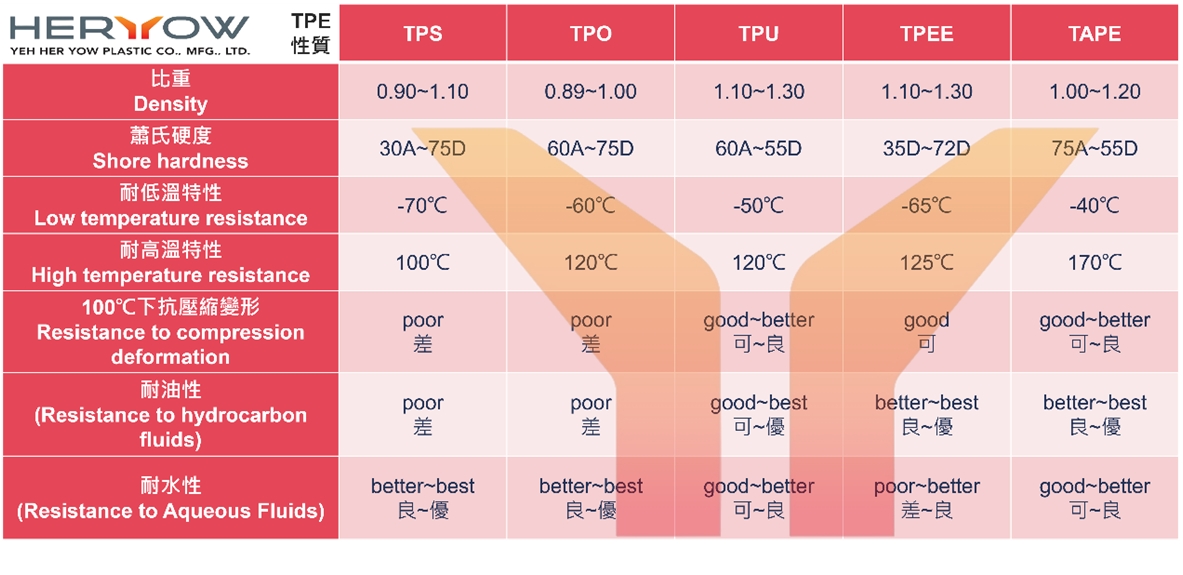
There are several categories of thermoplastic elastomer TPE: TPS, TPO, TPU, TPEE, TAPE. They also have different application ranges. Please refer to the table below.
Overmolded design
There are many aspects that need to be considered in overmolding design. It is not as simple as simply considering design and hardness. As mentioned above, the TPE thermoplastic elastomer will perform under different conditions such as temperature, humidity, sunlight, hardness, and oil resistance depending on the environment in which it is used. Under the condition of water resistance, there are many different selection points to consider. What kind of suitable materials should be selected? The above-mentioned conditions must be included in the selection conditions. The operation, the combination of different materials, and the assembly performance must also be considered, waterproof and dustproof, ergonomics, etc. It is also necessary to further consider the position of the inlet of the secondary processing, the flow direction, the size of the flow channel and space, and the processing conditions such as sink marks and air marks that are prone to appear on the appearance.
For example, the picture below is an example of a designed product. The purple one uses injection molding as the first processing, while the earthy yellow one uses overmolding.
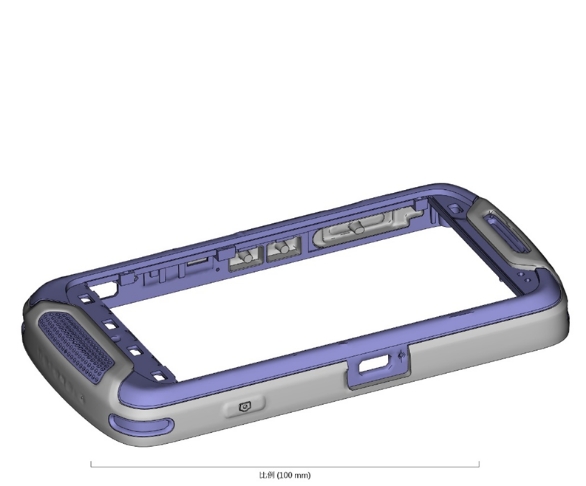
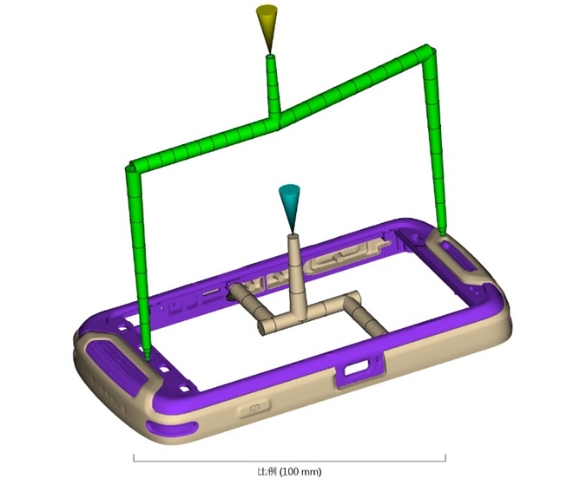
- First processing: injection molding
Which position should be filled in the first injection molding, which flow channels can be used for overmolding, whether the flow space is sufficient, etc.
- Second processing: overmolding
In the secondary processing of overmolding, it is also necessary to determine which position is suitable as a gate, which area to start filling, which areas the filling range will reach, etc.
Mold design
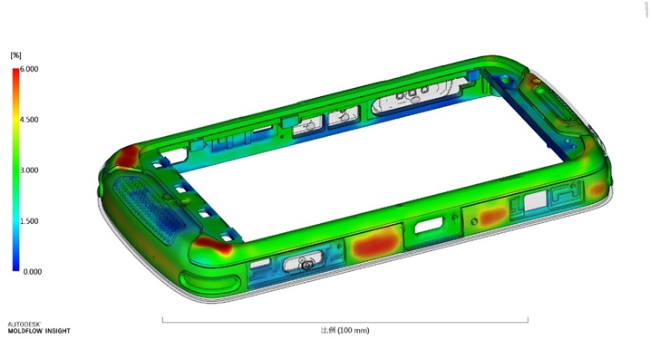
In mold design, it is even more important to consider the issue of deformation. From the first injection molding, there will be deformation of the base material and body. How to accurately control this deformation and control the deformation to a controllable level? Within the scope, this is a major focus.
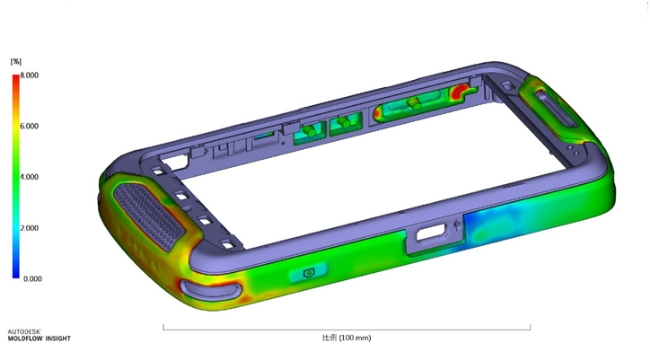
From a design perspective, differences in the thickness of the cladding material will change the effectiveness of the material's properties. The thicker part of the TPE wall can absorb more vibrations and feel softer to the touch. The thin-walled portion of the TPE will reduce the material's ability to absorb vibration and reduce the flow potential of the filling.
- Deformation of Overmolding
Overmolding also needs to consider the factor of deformation, which is more complicated because it includes the dimensional accuracy, material, temperature resistance of the first molding, etc., and then further evaluates the dimensional accuracy, inner thickness, etc. of the secondary molding. The flow area and the level of internal stress can be developed by combining the above reasons to develop good products. For example, the deformation in the picture below is the deformation amount of 1X and 10X. Only by enlarging the deformation amount can we more effectively evaluate whether inverse deformation processing and deformation processing are needed. The combined accuracy for subsequent use.
1 time deformation
10 time deformation
If you have overmolding needs, Yeh Her Yow Plastic Co. LTD., can help you. With our professional assistance, we can improve the reliability of your developed products.