Plastic Injection Molding
Plastics are mainly divided into two types: thermoplastic plastics and thermosetting plastics
Thermoplastics and Thermosets
Basically, plastics have a high dependence on temperature, so they respond to temperature,depending on the response, they can be divided into two categories:Thermoplastic plastics and thermosetting plastics:
Thermoplastic plastics: heat to melt, cool to solidify, and can be repeated.
Thermosetting plastics: Once heated to produce cross-chain reaction of molecular bonds and after it is cured and hardened, it will no longer change in temperature and will not melt due to temperature heating.
Influencing the properties of plastic materials, including in its manufacturing process:
- Processing temperature: Each plastic has its suitable processing temperature range. If the temperature is too low, it will be difficult to flow and cannot be filled. If the temperature is too high, it may cause thermal cracking.
- Flow velocity: when flowing, different degrees of shear rate will be generated due to the distribution gradient of velocity. If the shear rate is low, the plastic near the skin layer near the mold wall will easily cause stagnation, resulting in difficulty in filling. However, if the velocity is too fast, it will cause If the shear rate is too high, it will cause a high-speed increase in shear stress, which will cause the sub-bonds of the plastic polymer to be stretched excessively or even torn off, resulting in bond breaking, or excessive frictional heat (heat storage effect caused by viscosity) And cause thermal cracking of plastics.
- Volume shrinkage: The specific volume change produced during the phase change process can refer to the PVT diagram, which will cause a volume change in the molten plastic.
- Cooling rate: The molten plastic should be cooled with an appropriate mold temperature. Although a low mold temperature can shorten the molding cycle, if the cooling is too fast, the degree of crystallization will be reduced. In most cases, stress residues are likely to occur.
- Stress residue: Molecular stretching during flow, excessive pressure during holding pressure, thermal stress and shrinkage stress caused by uneven cooling during cooling.
- Ejection temperature: Each plastic has its appropriate ejection temperature range, and the ejection temperature refers to the temperature of the middle layer of its meat thickness. It must be cooled until the plastic has a sufficient rigidity temperature, so that it will not collapse when ejected. Cause deformation or top white, the general choice is below the heat distortion temperature of the plastic.
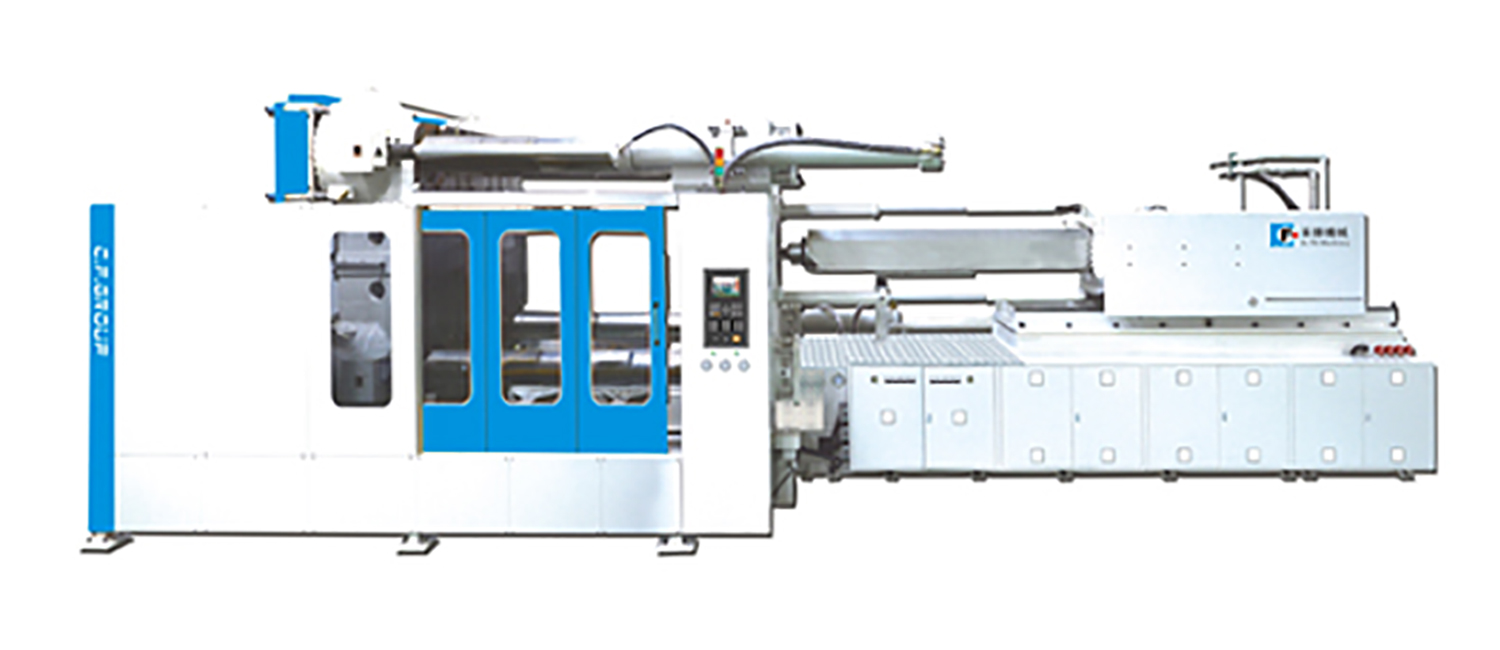
Injection molding processing method
Plastic products are very common in everyone's life, such as 3C products we use every day, such as mobile phone casings, computer casings, mice, etc.; daily household products, such as crisper boxes, portable water bottles; even large Various types of plastics are used in the shell panels of automobiles and motorcycles, outdoor furniture, etc. The wide application of plastic materials has already been integrated into our lives, and it can be said that they are closely related, and most thermoplastics are suitable for injection molding. The processing method of molding, however, has different characteristics in various types of plastics, and these different characteristics must be considered in the production process. Injection molding is a high-volume production cycle process, including feeding, melting, plasticizing, pressure injection (injection, extrusion, pressure holding), mold cooling, after mold opening, and finally the removal of finished parts and other stages For plastic processing, the impact of each step on the final product must be considered.
Advantages of Plastic Injection Molding
- High output and fast production speed
- Inexpensive materials and high selectivity
- Recyclable (thermoplastic material)
- lightweight
- Automated production
- High compatibility of mechanism design
Plastic injection molding process
The plastic injection molding process can be mainly divided into 5 steps: plasticization ⇒ injection ⇒ packing and holding ⇒ cooling ⇒ demoulding. These 5 stages will continue to circulate in the manufacturing process. With the trend of automated production, mass production can be efficiently produced. out the required plastic products.
1. Plasticization
The plastic raw material is melted at high temperature in the material tube. According to the characteristics of the selected plastic material, the plastic processing temperature is set on the injection molding machine, so that the plastic pellets are melted at the correct temperature.
2. Injection
The melted plastic raw material is filled and injected into the mold through the screw, and the plastic is shaped by using the mold design space. At this time, the parameters of the injection machine must be adjusted according to the plastic injection molding conditions or the mold condition to avoid subsequent dimensional mismatches, burrs, and material shortages. and other bad problems.
3. Packing and Holding
After the plastic raw materials are filled into the mold, continue to pressurize the space in the mold, mainly to ensure the tightness of these plastic raw materials, to avoid the backflow of raw materials, and to avoid problems such as shortage of materials and insufficient size of products.
4. Cooling of Mold
The product is rapidly cooled and shaped in the mold and continues to the plasticizing stage of the next mold.
5. Removal of the completed parts
Finally, the plastic product is completed, the mold is opened, and the product is taken out from the mold.