Talk about the plastic / What is the general plastic?
View the plastic
Today's market is full of a variety of materials. In the surroundings of life, most of them are dazzling plastic products, especially their high quality and low price, and their versatility, diversification, and plasticity. It is irresistible. In the development history of human civilization, from the Stone Age and Bronze Age in ancient times to the Iron Age when various steel products began to be used, it has undergone thousands of years of evolution. Until the middle of the 20th century, human beings on the earth changed their habit of using a large number of materials in just a few decades and began to use "polymer plastic" materials. In fact, we have already entered the unprecedented "Plastic Age" without knowing it.
Ever-changing polymer technology
Plastic materials are the result of the research and integration of the chemical industry. First, it is the petrochemical industry process of cracking, separating, purifying and manufacturing various monomer raw materials from light oil in crude oil. Then, through chemical synthesis and materials processing techniques, various types of plastic products are developed and manufactured. On the whole, they are not only light and durable, but also high in quality and low in price. They have become an indispensable part of human life. Durability, flame resistance, electrical breakdown strength, rigidity requirements, fire rating, etc., so in recent years, the demand for plastic materials by humans on the earth has continued to grow every year.
With the development of polymer chemical technology, under the research of major brand companies, we continue to invent and use different monomer raw materials to synthesize and manufacture diversified polymer materials, such as elastomers (Elastomer, rubber), fiber materials (Fiber), plastics (Plastics) and other categories. , This is the mystery of polymer chemical technology, such as: ABS universal plastics (Universal Plastics), PA nylon-engineering plastics (Engineering plastics), fiber-reinforced plastics (Fiber-reinforced plastics, referred to as FRP) and additives or rubber mixed with complex (such as carbon black, white smoke, plasticizers, stabilizers, antioxidants, cross-linking agents, flame retardants, fireproofing agents, anti-UV agents, etc.), after professional processing Programs can be developed to meet the needs of various special properties and uses of materials.
Polymerization reaction of polymer materials
Regarding general-purpose plastic materials, although the monomer raw materials are simple (as shown in the figure below), the ever-changing polymerization conditions and the combination of monomer raw materials can produce similar materials of various properties. For example, polyethylene (PE) can be divided into two types of polyethylene: high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE). Although I know the ins and outs of plastic materials, from the stages of cracking, separation, purification and polymerization of light oil, from plastic materials to various processing processes to products, the fields of these various sections are definitely professional areas, and plastic products have almost gone hand in hand with human beings. At least we need to know the true appearance of plastic products around our lives. This is the basic common sense of plastic products.
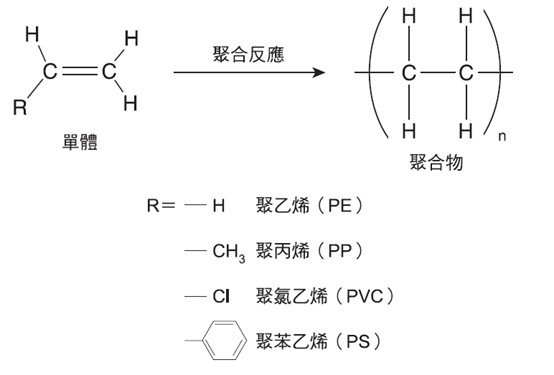
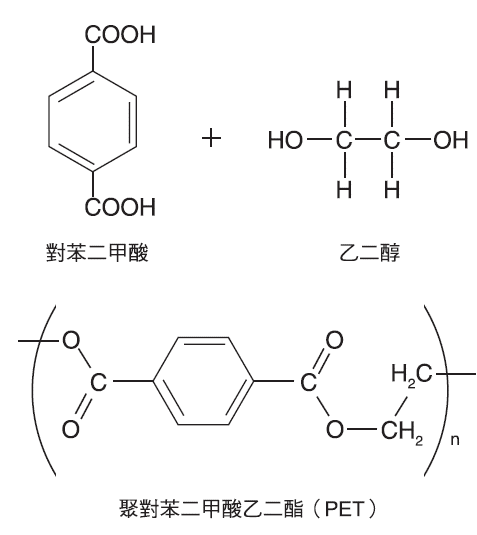
Schematic diagram of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) polymerization.
Understand common plastic materials in daily life
The types of plastic materials commonly used and commonly used at present are actually varied and numerous; the top four according to the total amount of plastics produced in the world, and sorted by their overall usage:
- 1: Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
- 2: Polyethylene (PE)
- 3: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
- 4: Polypropylene (PP)
- 5: Polystyrene (PS)
These four plastics are internationally known as Universal Plastics. However, another common material is polyethylene terephthalate (PET for short), which is PET plastic (PET bottle or polyester transparent film) and polyester fiber used in almost every household in the world every day. These five kinds of plastics are linear organic materials with high molecular weight (molecular weight of more than 10,000 or less than one million units), and they all have thermoplastic properties, so they are commonly called "thermoplastics".
These plastic materials are solid at room temperature. They are heated and softened to melt during processing, and can flow like a fluid and be injected into a specific mold under pressure. After cooling, they are formed into a solid shape. The scraps or waste of this "thermoplastic" product can be recycled for repeated processing and application. The bottom of the "thermoplastic" products on the market will be imprinted with international plastic numbers with numbers (as shown in the picture below), indicating the classification of materials that can be recycled and reused:
It is divided into six commonly used plastics, plus one other, and there are seven categories in total. What are the real features of the five commonly used plastics mentioned above? A brief introduction is as follows.
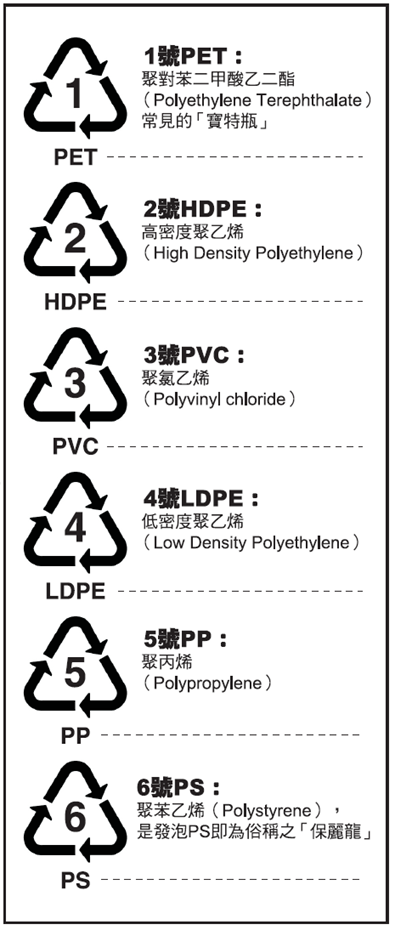
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
In the 1950s, DuPont produced tough Mylar film. At that time, it was mainly used for research materials, audio-visual recording tapes, X-rays or photographic negatives, etc. used in space;
Because of its rigidity, excellent toughness, light weight (less than one-tenth of glass), impact resistance, good chemical stability, easy to carry, and low energy consumption during production, it is a cheap and high-quality container material. Today, it is used in such a large amount in the world that it has almost reached the stage of being abused. Countries around the world are also under environmental protection issues and ESG sustainability. "PET bottle" recycling, through domestic synthetic fiber manufacturers, recycles "PET bottles" to make PET fibers (composed of the same chemical molecular chain, but polyester fibers with a lower molecular weight), and successfully promotes the products used in fabrics, and has won the recognition of the international community. More and more marine debris, from fiber cloth to film-like plastic, piles of plastic waste make sea pollution out of control. Out-of-control marine debris that is a turtle burial ground today could consume our homes tomorrow. Under the environmental protection issue of recycling, through 100% recycled polyester, waste P.E.T bottles (polyethylene terephthalate) are recycled and processed into fabrics. The following is the whole process of how to convert PET bottles into clothes:
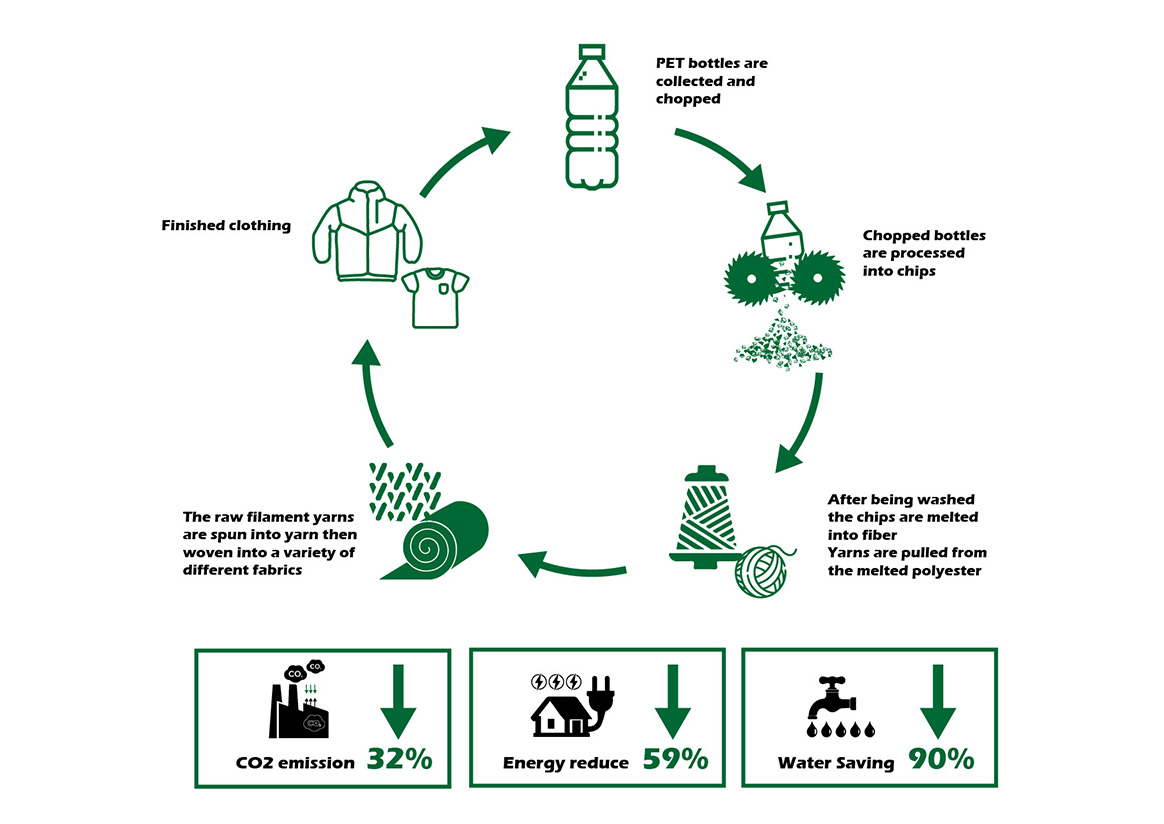
- Step1: Collect plastic bottles, remove the outer label, sterilize and dry, and then use a crusher and an extruder to cut into plastic particles
- Step2: Heat the plastic particles through the material tube and form a yarn through the extruding machine
- Step3: Weave yarn into fabric
This recycled product material has excellent drainage and quick-drying characteristics of the clothing fabric. In recent years, "PET bottles" PET materials have also been used in building materials. The popular pavilion "Far East Ark" at the International Flower Expo held in Taipei City in 2010~2011 is another major application of "PET bottles" in the history of world architecture.
Polyethylene (PE)
It can be divided into PE with various molecular weights and different degrees of side chains, providing physical properties such as melting point, hardness, and transparency of PE. Ultra-high molecular weight PE (fibers for fishing nets, industrial cloth films, parachutes, etc.); high-density PE (milk bottles, pudding boxes, chemical containers, etc.); medium-density PE, low-density PE (plastic bags, simple packaging boxes, food refrigerators, etc.), linear low-density PE, ultra-low density PE (packaging film, plastic wrap, etc.); Polymers can be adjusted by polymerization conditions and raw materials.
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Applied in non-food contact applications, such as various soft and hard water pipes, medical pipe fittings, home appliance wires, synthetic leather (cars, furniture sofas, leather bags, belts, shoe uppers, raincoats, transparent table mats, etc.), plastic floor tiles, etc. PVC itself has the advantages of cheap manufacturing, convenient processing, and good flame retardancy. It can be mixed with different proportions of plasticizers to adjust the softness of its products; or add inorganic powders such as stone powder, mineral fiber, and molybdenum disulfide to increase its rigidity and abrasion resistance. It also has the advantages of other plastic materials, so PVC is widely used today.
Polypropylene (PP)
Mainly used in battery casings, bottles, straws and other products. The molecular chain structures of PP and PE are very similar, and many physical and mechanical properties are better than PE. For example, the melting point of PP can be as high as 130~140°C, so it can be sterilized by steam or made into a special container for microwave heating. Most of the common straws and drinking cups are made of PP materials; even the national currencies of some countries use processed PP film to replace traditional banknotes, which has the advantages of oil resistance and oil resistance, which can greatly enhance the durability of use and reduce the degree of damage caused by human long-term use.

Polystyrene (PS)
PS has extremely low water absorption, good dimensional stability, light weight, and transparency; unfoamed PS is mainly used in toys, stirring rods, disposable tableware cups, and shells of some home appliances; foamed PS (EPS, commonly known as Styrofoam) is foamed by adding a foaming agent during the manufacturing process to a ratio of 20 to 100 times. It is used for packaging home appliances, information products, and cakes. , because the only way to deal with waste Styrofoam is high-temperature incineration. Many advanced countries in the world have begun to ban Styrofoam for disposable tableware due to environmental pollution and other reasons. However, Styrofoam is still widely used in fish farming because of its good durability, good weather resistance, and good buoyancy.
PVC needs to add plasticizer
Among the five major plastic materials mentioned above, except for PVC materials, they are all pure polymer materials, which are used in different industries based on their physical and chemical properties, and can be made into our desired products without any additives during the manufacturing process. Only PVC needs to add many additives, such as the necessary plasticizer, the amount of plasticizer (about 5~30%) to adjust the use of different hardness, also need to consider the environment in which the product is used, add stabilizers to prolong the service life, etc.
There are many types of plasticizers added in the PVC manufacturing process. The plasticizer is commonly called DOP in the industry. The main one is i-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP for short). Some items made of flexible PVC synthetic leather, such as brand new sofas, shoes, leather bags or raincoats, etc., we often smell a strong plastic smell. In fact, this is the smell of the plasticizer DEHP.
PVC has the advantages of other plastic materials, so PVC is widely used today. However, the existing PVC finished products are plastic products processed through various complex formulas (plasticizers, stabilizers, inorganic additives, pigments, etc.). However, the mixing of these additives does not have any chemical bonding, and the additives are easy to migrate to the product surface over time. In particular, the toxicity of DEHP plasticizer should be paid attention to; although it is impossible to measure whether the amount of plasticizer dissolved will exceed the "Tolerable Daily Intake" (Tolerable Daily Intake), so plastics containing DEHP plasticizers must not be mixed with For long-term contact with food or human body, wash your hands immediately after contact with related PVC products, and avoid ingesting plasticizers and causing residues in the human body.
After use, PVC cannot be directly recycled and reused. In addition, due to the organochlorine contained in the material, after high temperature (incineration) treatment of PVC, the PVC after thermal cracking will produce highly toxic dioxin (2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, referred to as dioxin), which has been proven to cause health hazards to organisms. Chlorine material) application, in EU countries, is also the RoHS lead-free and halogen-free specification for electronic products.
The proportion of plasticizer contained in soft PVC is higher than that of rigid PVC. The plasticizer contained in it will follow the daily use of the product, especially waste PVC products, which will gradually escape into the air or dissolve into groundwater or rivers in the wind and sun. The plasticizer DEHP is a kind of environmental hormone. If it accumulates too much, it will cause environmental hazards. If it exceeds the "Tolerable Daily Intake", it will cause harm to living organisms. This is also the most concerned issue of waste disposal and environmental protection in society.
Matters needing attention when using plastic
The above-mentioned five types of plastic materials that are commonly used are easy to use, durable, versatile, cheap and high-quality, and are worth cherishing and using; however, please remind the public to avoid misuse of plastic materials, which will cause danger and cause permanent damage and damage to the environment, because their shortcomings can never be changed. There are a few that should be paid special attention to, such as:
- 1. Thermoplastics with low melting point are easily deformed or melted by heat (except for HDPE and PP, which can be sterilized by steam), and should be avoided in high temperature (above 60~80°C) environments.
- 2. Flammable organic materials must never be in direct contact with fire sources, because plastic is a material with a low oxygen index and is extremely flammable. (Although PVC is a flame-retardant material), it will catch fire and burn when exposed to high heat, producing a large amount of black smoke (carbonized gas), especially PVC will produce the highly toxic century-old dioxin.
- 3. Avoid contact with organic solvents (PET, PS, PVC, etc. are soluble in organic solvents such as acetone, toluene, etc.) or grease, because these materials are straight-chain (uncrosslinked) organic polymers, so they will be dissolved when they encounter smaller molecular materials.
Taiwan's plastic material technology is already a leading power in the world. Although Taiwan does not have natural resources such as oil, it has stable plastic materials, raw material sources and product application technologies, especially in the development of cross-field material application technologies. Taiwan has a unique environment and competitive advantages for the development of new products. It also has decades of development and application in the plastic field. Yeh Her Yow Company definitely has its advantages in research and development and production.